La-la-la! Biology makes me so happy!

Biology? more like BYE-ology? don't worry you have come to the right place!




Baffled by some of the words? Check out the Key terms page
Clinical Obesity
overweight to a degree which causes medical complications
A fatty or waxy organic compound that is readily soluble in nonpolar solvent (e.g. ether) but not in polar solvent (e.g water). Its major biological functions involve energy storage, structural component of cell membrane, and cell signaling.
LIPIDS: Definition
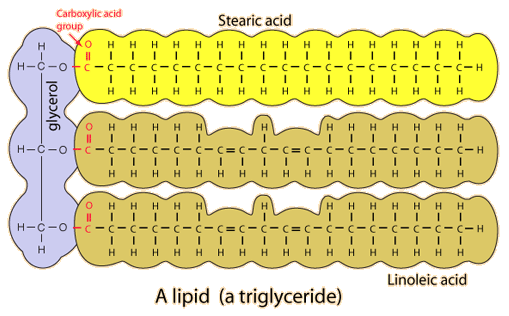
Figure one " Trygliceride

Figure 2: Tricglyceride

FATTY ACIDS: definition:
Fatty acids are the building blocks of the fat in our bodies and in the food we eat. During digestion, the body breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can then be absorbed into the blood. Fatty acid molecules are usually joined together in groups of three, forming a molecule called a triglyceride. (figure ONE & 2) Triglycerides are also made in our bodies from the carbohydrates that we eat.
Fatty acids have many important functions in the body, including energy storage. If glucose (a type of sugar) isn't available for energy, the body uses fatty acids to fuel the cells instead.
What are "Lipids" also known as?
Fats, oils, waxes, and sterols are collectively known as lipids.
True fats contain only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
The molecules of lipids like these consist of a glycerol molceule; attached to three fatty acid molecuels.
This is known as a triglyceride (Scroll UP for more details)
Overview of Molecular Biology