
Absolutely EVERYTHING you need to know about energy and much much more!
Hannah's Energetics Emporium



Entropy? Enthalpy? more like gibberish!?!! Don't worry you have come to the right place!


Hess's Law Main Rule
Hess's Law of Constant Heat Summation (or just Hess's Law) states that regardless of the multiple stages or steps of a reaction, the total enthalpy change for the reaction is the sum of all changes. This law is a manifestation that enthalpy is a state function. (chemwiki)



Intermediate


DONT FORGET
Does not matter which route you take; the end product will ALWAYS be the SAME!


Intermediates
The Intermediates refer to the components in the reaction which are halfway between reactants and being converted into the products.


Law of Conservation of Energy
The Enthalpy change of a reaction is dependent on the difference between the enthalpy of the products and the enthalpy of the reactants.
Enthalpy Change of a reaction is the same despite the route which is taken. It can go directly to the product or through an intermediate
This law refers to the law of conservation of energy.
Law of enthalpy of combustion can be used to find out enthalpy changes that can't be measured directly.


Law of conservation of energy : DIAGRAM Diagram A



Law of conservation of energy : EXAMPLE
Enthalpy of combustion of both carbon and carbon monoxide can be measrued directly, combustion of carbon to carbon monoxide cannot be measured directly.
(diagram A)
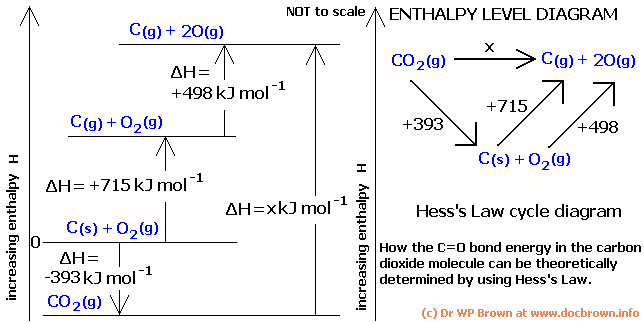
To find out delta H of reaction add up all enthalpy values
if arrow is facing wrong way flip it and change sign of delta H


Solving by Simultaneous Equation
Write out known equations and then manipulate them to get required equation.
1) C(s)+ O2(g) ----> CO2(g) delta H= -394 kJ mol-1
2) CO(g) + 1/2 O2(g) ---> CO2(g) delta H= -283 kJ mol-1
Subtract 2 from 1
C(s) + 1/2 O2 (g) - CO (g) = 0 delta H = -394 - (-283) kJ mol-1
Rearrange equation
C(s) + 1/2 02(g) ----> CO delta H = -111 kJ mol -1
